1528. 重新排列字符串#
问题描述#
给你一个字符串
s和一个 长度相同 的整数数组indices。请你重新排列字符串
s,其中第i个字符需要移动到indices[i]指示的位置。返回重新排列后的字符串。
示例 1:
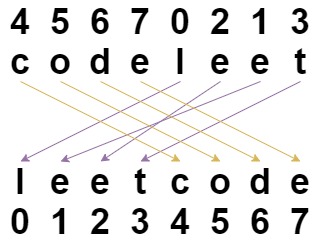
输入:s = "codeleet",indices= [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3] 输出:"leetcode" 解释:如图所示,"codeleet" 重新排列后变为 "leetcode" 。示例 2:
输入:s = "abc",indices= [0,1,2] 输出:"abc" 解释:重新排列后,每个字符都还留在原来的位置上。示例 3:
输入:s = "aiohn",indices= [3,1,4,2,0] 输出:"nihao"示例 4:
输入:s = "aaiougrt",indices= [4,0,2,6,7,3,1,5] 输出:"arigatou"示例 5:
输入:s = "art",indices= [1,0,2] 输出:"rat"
提示:
s.length == indices.length == n1 <= n <= 100s仅包含小写英文字母。0 <= indices[i] < nindices的所有的值都是唯一的(也就是说,indices是整数0到n - 1形成的一组排列)。
解题思路#
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
测试数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |